The kind of organization depend of the various tasks
which will be perform (business functions). They are:
Each business organization have a specification, that is division of work - each employee focuses on a specific task.
A major component in each organization is the ethics. People and organizations, such who use computers are morally responsible and can be held accountable just as the operators of the motor vehicle can be held accountable for their actions. In some instances, specific laws govern the use of computers. Because computers aree relatively new. The ethics within an organization have three major concepts:
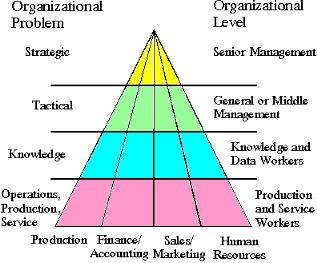
As it has mentioned in the first lecture, the organization is hierarchical and structured. The hierarchy of responding and authority relationship is developed to assume that the work is completed. Organization differ in terms of how much authority is concentrated in each layer.
People at the bottom of the hierarchy report to those on the next level, and so on the up to senior management. The senior management is the people with the most authority and make long-range decisions for the future of the organization.
The next lower layer is the middle management group organized into specialized divisions which carries out the programs and plans of senior management by supervising employees.
In the middle of the hierarchy in an organization are knowledge and data workers. They design the firm's product or service and do much of the paperwork that running a business involves.
The lowest layer is production or service workers who actually produce the firm's products or services.
On the other hand within an organization is a network of personal relationships - birthday parties, births, new hires and retirements. This is the informal structure in organization.
Strategic-level systems help senior managers plan. Some problems are clearly strategic because they involve questions of organizational goals, products, services and long-term survival. Such problems in organization are typically handled by senior management, and often strategic-level systems and applications are developed. Strategic-level systems might be used in deciding whether to introduce new products, invest in new technology, or more to a new location.
Middle management systems help control an organization's day-to-day activities. In an organization are problems, that are clearly tactical, because they involve questions of how to achieve goals and how to control and evaluate the process of achieving goals. These problems involve the development of tactical,
or management support systems. Tactical systems might be used in such applications as monitoring sales to see if annual or quarterly targets were met or reviewing departmental budgets to make sure the firm is not
wasting its resources.
Knowledge systems are used by knowledge workers (such as engineers, doctors, lawyers or scientists) in business organizations to solve questions requiring knowledge and technical
expertise.
Operational systems are used in manufacturing and service delivery to solve problems related to operations, services, and production.
Goods-producing typically develop a manufacturing and production function with a division or department of manufacturing that specializes in the production of the goods or services that the firm produces for the customers. In manufactoring, IS are used to process customer orders, develop production schedules, control inventory levels, and monitor product quality. The typical production process can be divided into three stages: inbound logistics, production and outbound logistics.
Many firms are trying to create a seamless manufacturing process by integrating the various types of automated manufacturing systems using computers and communication technology. The data produced in one system are immediately available to be used by other system. One of the most popular uses of computers in manufacturing is to keep track of the location and number of component parts and finished products held in inventory by firms. By tracking exactly what items are in stock and where they are located, inventory control systems enable business to keep just the right number
of parts and products on hand to fill orders.
Here another typical manufacturing and production information systems arranged by the organizational level of the problem.
ties location applications
Competitor scanning and intelligence
Computer integrated manufacturing
monitory control systems
accounting systems
acity planning
or-costing systems
Production scheduling
Computer-aided manufacturing systems(CAM)
Engineering workstations
Numerically controlled machine tools
Robotics
Shipping systems
Labor-costing systems
Materials systems
Equipment maintenance systems
Quality control systems
The basic purpose of the sales and marketing function is to sell the product and service to customers. Identifying market needs, locating potential customers and satisfying those customers require a great deal of information that must be effectively analyzed and applied. There are three steps involved in sales and marketing: identifying and creating a market, developing it, and maintaining it.
In marketing, Information Systems are used to develop new goods and services (product analysis), determine the best location for production and distribution facilities (place or site analysis), determine the best advertising and sales approaches (promotion analysis), and set product prices to get the highest total revenues (price analysis). There are several ways in which information systems help firms become more effective markets.
Economic forecasts
Competitor scanning applications
Pricing strategy decision support systems
Sales personnel management systems
Marketing data analysis
Order entry systems
Point-of-sale systems(POS)
Telemarket systems
Credit information systems
 A business organization is a complex, formal organization whose aim to produce products or services for a profit. It depends heavily on their surrounding environment. As well as government regulation, economic and political conditions and technological development business environment includes also people, or entities with which the firm is more directly involved, such as customers, suppliers, and competitors.
A business organization is a complex, formal organization whose aim to produce products or services for a profit. It depends heavily on their surrounding environment. As well as government regulation, economic and political conditions and technological development business environment includes also people, or entities with which the firm is more directly involved, such as customers, suppliers, and competitors.
See for more information Examples of Business Information Systems
In-Bound logistics
Production
Out-Bound logistics
Organizational level systems
Strategic-Level Systems
Tactical Systems
Knowledge Systems
Operational Systems
Type information systems
Production Technology scanning applications
Manufacturing resource planning
Computer-aided design systems (CAD)
Purchase/receiving systems
Description
Deal with the firm's long-term manufacturing goals, such as where to locate new plants or whether to invest in new manufacturing technology.
Deal with the management and control of manufacturing and production cost resources.
Create and distribute design knowledge or expertise to drive the production process.
Deal with the status of production tasks.
Organizational level systems
Strategic - Level Systems
Tactical Systems
Knowledge Systems
Operational Systems
Type information systems
Demographic market forecasting system
Sales management systems
Marketing workstations
Sales person support systems
Description
Monitor trends affecting new products and sales opportunities, support planning for new products and services and monitor the performance of competitors.
Support market research , advertising and promotional campaigns, and pricing decisions and analyze sales performance and the performance of the sales staff.
Support marketing and analysis workstations.
Assist in locating and contacting prospective customers, tracking sales, processing orders, and providing customer service support.